

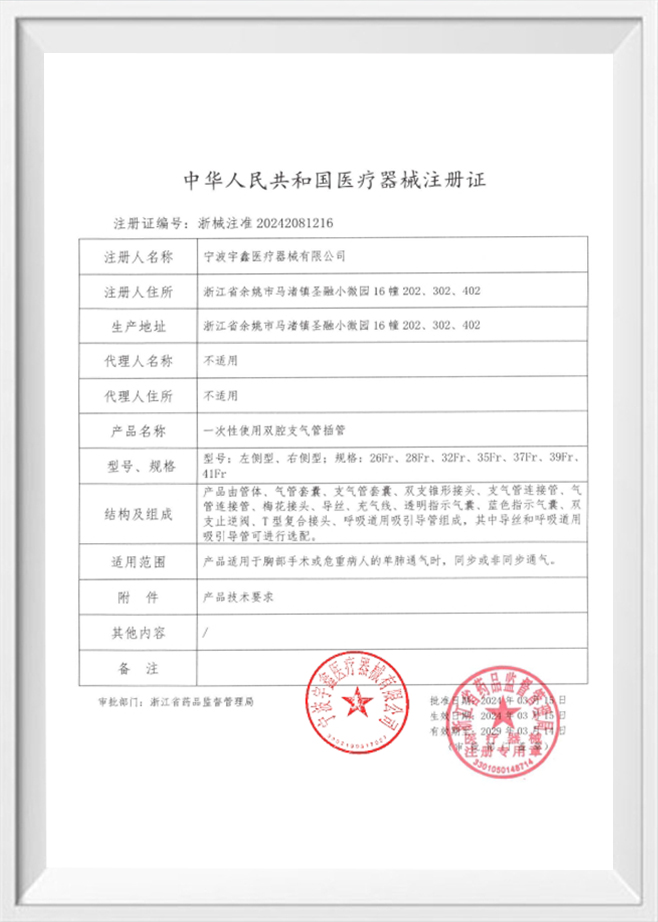
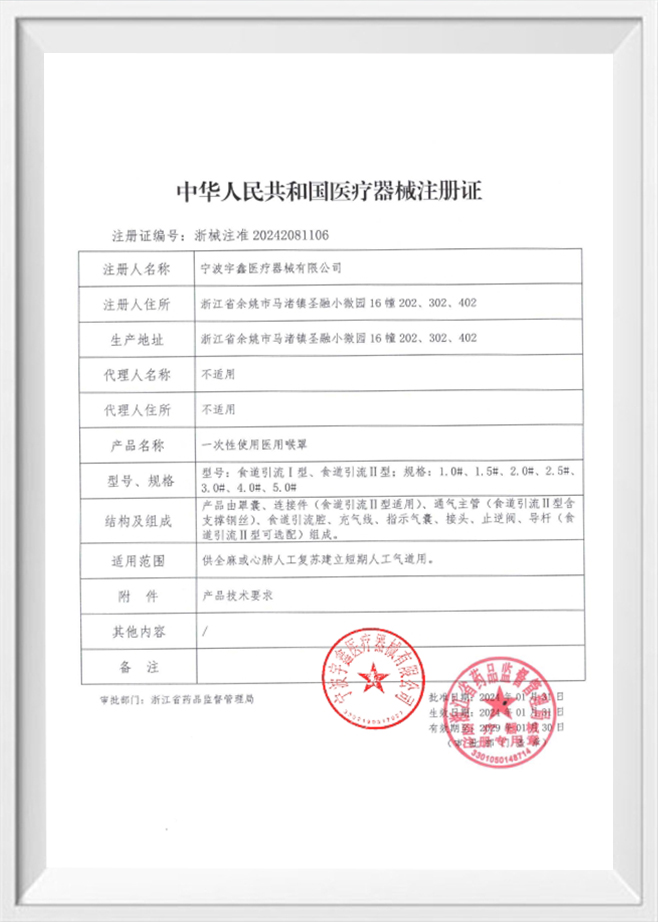



Introduction to Closed Suction Catheters Closed suction catheters are medical devices used to clear the airways of patie...
View MoreIntroduction to Silicone Resuscitators Silicone resuscitators, also known as manual resuscitation bags or Ambu bags, are...
View MoreUnderstanding Gas Leakage in Anesthesia Delivery Anesthesia masks are essential components in inhalation anesthesia syst...
View MoreGeneral characteristics of silicone reservoirs A silicone reservoir is a container or flexible storage component manufac...
View MoreIntroduction to Cervical Ripening and the Role of Cervical Ripening Balloon Cervical ripening is a critical part of the ...
View MoreWhat Are Breathing Filters and HMEs, and Why Are They Important?
Breathing filters are medical devices designed to reduce the risk of infection transmission and contamination within respiratory systems. They are commonly used in anesthesia, intensive care, and respiratory therapy to protect both patients and medical equipment. These filters are typically installed between the patient’s airway and the breathing circuit, serving as a barrier to microorganisms, particulates, and other contaminants. Breathing filters play an important role in clinical environments where cross-contamination can occur, especially when multiple patients share the same respiratory equipment or when equipment is reused after sterilization.
HME stands for Heat and Moisture Exchanger. This device is used in respiratory care to retain the patient’s exhaled heat and moisture and return it during inhalation. In normal breathing, the upper airway warms and humidifies inhaled air. However, when a patient is intubated or uses a tracheostomy, this natural function is bypassed. An HME helps to replicate this natural process by capturing heat and moisture from exhaled air and then releasing it back into the inhaled air, helping to maintain the humidity and temperature levels necessary for airway health.
Maintaining appropriate humidity and temperature in inhaled air is essential for preserving the function of the respiratory mucosa. Without adequate humidification, the airway can become dry, which may lead to thickened secretions, increased airway resistance, and potential complications such as mucosal injury. In clinical settings where patients are mechanically ventilated or under anesthesia, the need for humidification is heightened because the natural warming and humidifying function of the upper airway is bypassed. HMEs support the patient by helping to prevent dryness and maintain the condition of the airway lining.
Breathing filters are used to reduce the spread of infectious agents and prevent the contamination of respiratory circuits and ventilators. In operating rooms and intensive care units, the use of breathing filters can lower the risk of cross-infection by trapping bacteria, viruses, and other particles. This protective effect is particularly important during procedures such as intubation or when patients require prolonged mechanical ventilation. In addition to protecting patients, breathing filters also help safeguard healthcare workers by minimizing the risk of exposure to airborne pathogens that may be released during respiratory procedures.
Breathing filters are available in different designs and specifications depending on their intended use. Some filters are designed primarily for bacterial and viral filtration, while others focus on particle filtration or combined functions. In anesthesia circuits, filters are often placed at the patient end to protect both the patient and the anesthesia machine. In mechanical ventilation, filters may be used to protect the ventilator from contamination and to reduce the risk of ventilator-associated infections. The choice of filter depends on clinical needs, the patient’s condition, and the type of respiratory support being provided.
When selecting HMEs and breathing filters, compatibility with the respiratory circuit is essential. HMEs are typically placed between the endotracheal tube and the breathing circuit, and they must fit securely to prevent air leakage and ensure effective humidification. Breathing filters must also be compatible with the breathing circuit to maintain a closed system and ensure that filtration performance is not compromised. Proper connection and secure fitting are critical for the safety and effectiveness of both HMEs and filters, especially during long-term ventilation or in high-risk environments such as operating rooms and ICUs.
Manufacturing breathing filters and HMEs requires strict adherence to medical quality and safety standards. High-tech medical enterprises, such as Ningbo Yuxin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., which is located in Yuyao, Zhejiang Province, often operate clean workshops and laboratories to ensure product quality. With a 100,000-level standard clean workshop and a 10,000-level laboratory, production processes can be controlled to meet regulatory requirements and reduce contamination risks. Advanced equipment such as silicone injection molding machines, plastic extruders, and flat vulcanizers support the production of medical respiratory consumables, including respiratory filters and heat and moisture exchange filters.
Respiratory filters and HMEs are used across a range of clinical scenarios, including anesthesia, mechanical ventilation, and respiratory therapy. In anesthesia, these devices are used to protect the patient and equipment during surgery. In intensive care units, they help maintain airway moisture and protect against contamination during prolonged ventilation. In respiratory therapy, HMEs can support patients with compromised airway function by helping maintain humidity levels. In each scenario, the correct selection and use of these devices contribute to patient safety and treatment effectiveness.
Proper use and timely replacement of HMEs and breathing filters are crucial to maintaining their effectiveness. HMEs can become saturated with moisture over time, which may reduce their ability to exchange heat and moisture. Breathing filters can also become blocked by secretions or particulates, leading to increased airway resistance. Clinical guidelines typically recommend regular monitoring and replacement based on patient condition and duration of use. Healthcare providers should also ensure that the devices are used in accordance with manufacturer instructions and that connections are secure to prevent leaks or disconnection during treatment.
| Feature | Breathing Filter | HME (Heat and Moisture Exchanger) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Filtration of bacteria, viruses, and particles | Retention and return of heat and moisture |
| Typical Use | Prevent contamination and cross-infection | Maintain airway humidity and temperature |
| Placement | Between patient and breathing circuit | Between endotracheal tube and breathing circuit |
| Key Considerations | Filtration efficiency and airflow resistance | Moisture retention capacity and resistance |
The production of respiratory filters and HMEs requires a controlled manufacturing environment and strict quality control measures. A clean workshop and professional laboratory testing are essential to ensure that products meet medical standards. Ningbo Yuxin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. is equipped with advanced production equipment and a clean workshop, which supports the manufacturing of various respiratory consumables such as heat and moisture exchange filters, respiratory filters, and respiratory extension tubes. This level of production capability helps ensure that products are manufactured in a controlled environment, which supports consistency and safety in clinical use.
Breathing filters and HMEs are part of a broader respiratory system that includes airway devices such as endotracheal tubes, laryngeal masks, and airway tubes. In clinical practice, these components work together to support ventilation and airway management. For example, an endotracheal tube or laryngeal mask may be used to secure the airway, while an HME helps maintain humidity and a breathing filter protects against contamination. The selection of compatible components is important for maintaining a safe and effective respiratory system, especially during procedures like intubation and mechanical ventilation.
In hospitals and clinics, respiratory consumables are often used alongside other medical devices and equipment. For example, in operating rooms, anesthesia circuits may be connected to ventilators and monitoring systems. In these settings, it is important to ensure that all components are compatible and that the respiratory circuit remains closed and secure. The inclusion of respiratory extension tubes and closed suction systems can further support airway management and reduce the risk of contamination. This integrated approach to respiratory care helps maintain patient safety and supports clinical efficiency.
Many healthcare providers require customized respiratory accessories to meet specific clinical needs. OEM customization can include different materials, sizes, and designs for respiratory filters, HMEs, and other airway products. Companies that provide OEM customization, like Ningbo Yuxin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., can work with customers to develop silicone and plastic accessories tailored to specific applications. This capability supports the development of products that meet unique clinical requirements and supports the adoption of respiratory devices in different healthcare environments.
Breathing filters and HMEs can contribute to clinical workflow efficiency by simplifying respiratory management. Using an HME can reduce the need for external humidification systems, while breathing filters can reduce the need for frequent equipment disinfection and circuit changes. In busy clinical environments, these devices support a more streamlined approach to airway management. When combined with reliable airway devices and accessories, they help create a more efficient respiratory care process, supporting patient safety and operational productivity. This efficiency is important in high-demand areas such as operating rooms, intensive care units, and emergency departments where time and resources are critical.
In medical facilities, respiratory consumables are often used alongside various support equipment, including scissor lift tables and hydraulic lift tables. These tables are used for patient positioning, equipment placement, and ergonomic support during procedures. Proper positioning can support airway management and facilitate the use of respiratory devices such as endotracheal tubes, laryngeal masks, HMEs, and breathing filters. The coordination between respiratory consumables and support equipment contributes to a safer and more efficient clinical environment, especially during anesthesia and surgical procedures where precise positioning is important.
FAQ
Q: How do breathing filters and HMEs differ in their primary clinical roles?
A: Breathing filters focus on reducing contamination by trapping bacteria, viruses, and particles within the respiratory circuit, while HMEs are designed to conserve the patient’s exhaled heat and moisture and return it during inhalation. In clinical practice, both devices can be used together to support safe and effective ventilation, especially during anesthesia and mechanical ventilation.
Q: Why is the choice of material important for HMEs and breathing filters?
A: Material affects factors such as filtration efficiency, moisture retention, airflow resistance, and biocompatibility. Medical-grade silicone and high-quality plastics are commonly used in respiratory consumables due to their stability, flexibility, and safety. A controlled manufacturing environment and strict testing, like those in a clean workshop and laboratory, help ensure the materials meet medical standards.
Q: Can HMEs and breathing filters be used interchangeably in the respiratory circuit?
A: HMEs and breathing filters are not interchangeable because they serve different functions. HMEs are intended to provide humidification and temperature control, while breathing filters are intended to prevent contamination. In many clinical situations, they are used in combination, but the selection and placement should follow clinical protocols and device compatibility requirements.
Q: How do breathing filters and HMEs impact airway resistance during ventilation?
A: Both breathing filters and HMEs introduce some resistance to airflow. The extent of resistance depends on design, size, and the level of moisture or particles captured. Proper monitoring is essential, as increased resistance may affect ventilation efficiency. In some cases, devices may need to be replaced or adjusted to ensure adequate airflow and patient comfort.
Q: What are the key considerations for replacing HMEs and breathing filters during long-term ventilation?
A: Replacement depends on factors such as moisture saturation, secretion buildup, and airflow resistance. HMEs can become saturated over time, which reduces their humidification efficiency, while filters may become blocked by particles and secretions. Clinical guidelines recommend regular monitoring and timely replacement to maintain performance and reduce infection risk.
Q: How does a clean workshop and laboratory testing contribute to the safety of breathing filters and HMEs?
A: Clean workshop environments and laboratory testing help ensure that respiratory consumables are manufactured under controlled conditions, reducing contamination risk and improving consistency. Equipment such as silicone injection molding machines and plastic extruders, along with a 10,000-level laboratory, support strict quality control for products like heat and moisture exchange filters, respiratory filters, and other accessories.
Q: In what clinical situations are breathing filters and HMEs most commonly used together?
A: They are often used together in anesthesia and intensive care settings where patients require mechanical ventilation. HMEs help maintain airway humidity and temperature, while breathing filters reduce the risk of contamination in the breathing circuit. This combination supports airway health and infection control during surgical procedures and long-term ventilation.
Q: How do respiratory extension tubes and closed sputum suction systems interact with breathing filters and HMEs in a complete respiratory setup?
A: Respiratory extension tubes and closed sputum suction systems are used to support airway management and reduce contamination risk during suctioning. When used with breathing filters and HMEs, they help maintain a closed respiratory circuit, ensuring that humidification, filtration, and airway access are maintained without compromising safety or performance.