

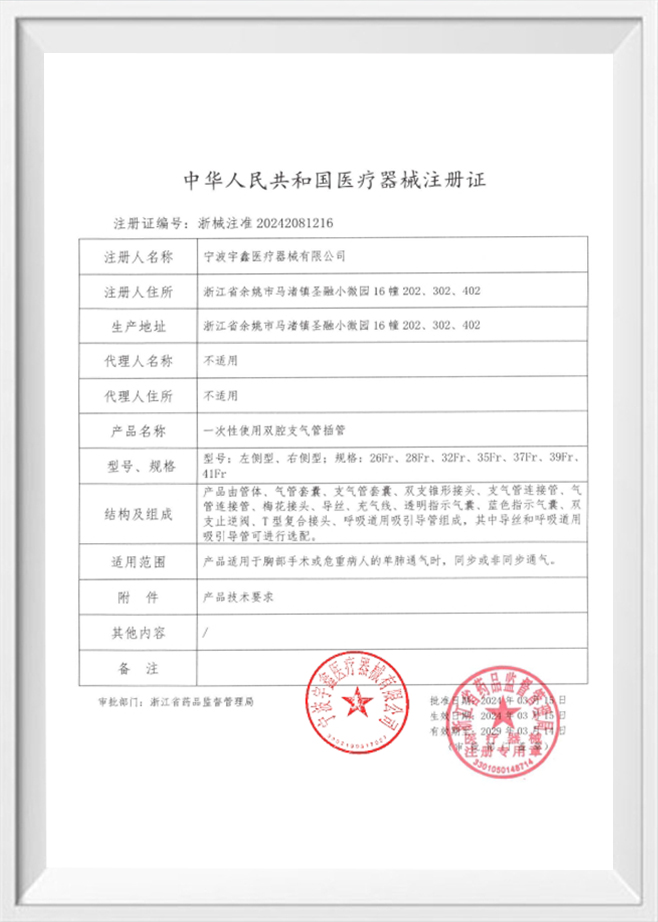
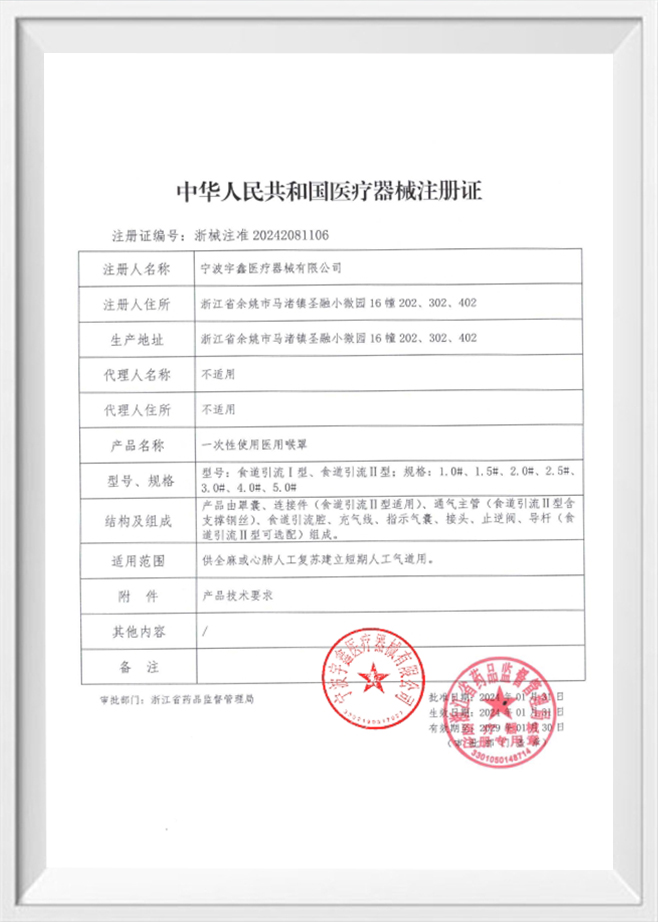



Introduction to Closed Suction Catheters Closed suction catheters are medical devices used to clear the airways of patie...
View MoreIntroduction to Silicone Resuscitators Silicone resuscitators, also known as manual resuscitation bags or Ambu bags, are...
View MoreUnderstanding Gas Leakage in Anesthesia Delivery Anesthesia masks are essential components in inhalation anesthesia syst...
View MoreGeneral characteristics of silicone reservoirs A silicone reservoir is a container or flexible storage component manufac...
View MoreIntroduction to Cervical Ripening and the Role of Cervical Ripening Balloon Cervical ripening is a critical part of the ...
View MoreApplications of Obstetric Balloons in Postpartum Hemorrhage Management
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) remains one of the most urgent challenges in obstetric care, as it can lead to rapid blood loss and severe physiological stress. Obstetric balloons are medical devices used to help manage bleeding after childbirth, particularly when first-line measures such as uterine massage and uterotonic drugs are not fully effective. The balloon is inserted into the uterus and then inflated with fluid to apply pressure to the uterine walls, which can help reduce bleeding by promoting compression of blood vessels and supporting clot formation. This method is often considered when bleeding is persistent and other interventions need to be supplemented.
There are several types of obstetric balloons used for PPH management, including cervical dilation balloons, balloon stents, and uterine cold filling balloons. Each type has specific design features suited to different clinical needs. Cervical dilation balloons are primarily used to assist with cervical dilation but may also support bleeding control in certain situations. Balloon stents and uterine balloons are designed to provide direct pressure inside the uterine cavity. These devices may be selected based on factors such as the cause of bleeding, the size of the uterus, and the clinical setting. OEM customization can support variations in balloon size and material to meet specific requirements.
Placement of an obstetric balloon typically requires careful clinical assessment and aseptic technique. The device is introduced into the uterine cavity through the cervix, and once properly positioned, it is gradually filled with sterile fluid to achieve the desired pressure. The volume of inflation is adjusted according to the patient’s uterine size and the response in bleeding control. During the procedure, healthcare providers monitor vital signs and bleeding volume, and the balloon may be left in place for a period of time to stabilize the patient. Proper management of the balloon, including monitoring for displacement or leakage, is important for maintaining its effectiveness and ensuring patient safety.
Obstetric balloons are commonly used in cases of PPH caused by uterine atony, placenta accreta spectrum, or other conditions that lead to excessive bleeding. When uterine muscle tone is insufficient to compress blood vessels after delivery, a balloon can provide mechanical support to reduce blood loss. In cases where the placenta is abnormally attached or where there is risk of retained placental tissue, balloons can help control bleeding while additional interventions are planned. They may also be used in conjunction with other methods such as uterotonic drugs, surgical interventions, or uterine artery embolization, depending on the clinical scenario.
One of the key advantages of obstetric balloons is their ability to provide rapid mechanical compression in emergency settings. When bleeding is severe, timely intervention is essential to prevent hemodynamic instability and reduce the need for more invasive procedures. Obstetric balloons can be inserted relatively quickly and can help stabilize the patient while additional treatments are arranged. In resource-limited settings, balloons can offer a practical option for bleeding control when advanced surgical or interventional radiology resources are not immediately available. The device can also reduce the need for blood transfusion by helping to control bleeding early in the course of PPH.
Obstetric balloons must be made from materials that are biocompatible, flexible, and able to withstand inflation without rupture. Silicone and medical-grade plastics are commonly used due to their stability and compatibility with body tissues. The manufacturing process must ensure consistent thickness, elasticity, and sealing to prevent leakage. Ningbo Yuxin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. operates a 100,000-level clean workshop and a 10,000-level laboratory, which supports controlled production and testing. Advanced equipment such as silicone injection molding machines and flat vulcanizers help produce balloons and related accessories with consistent quality. OEM customization allows for variations in balloon size and design to meet specific clinical requirements.
| Balloon Type | Typical Use | Clinical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical Dilation Balloon | Assists cervical dilation and can support bleeding control | Suitable for situations where cervical opening is needed |
| Balloon Stent | Provides internal support to reduce bleeding | May be used when additional stabilization is required |
| Uterine Cold Filling Balloon | Controls bleeding by uterine compression with cooled fluid | Requires careful monitoring of temperature and pressure |
Monitoring is essential during balloon therapy to ensure the device is working as intended and to detect potential complications. Vital signs, uterine tone, and bleeding volume are regularly assessed. The inflation pressure and volume are adjusted based on clinical response. Complications such as balloon displacement, leakage, or infection can occur, so maintaining sterile technique and careful observation is important. In some cases, the balloon may need to be removed or repositioned if bleeding continues or if there are signs of adverse effects. Close communication among the clinical team supports timely decision-making and patient safety.
Obstetric balloons are often used as part of a broader PPH management strategy. In many cases, balloon therapy is combined with uterotonic drugs to enhance uterine contraction and reduce bleeding. Surgical interventions such as uterine compression sutures or hysterectomy may be considered if bleeding is not controlled. In some settings, interventional radiology procedures such as uterine artery embolization may be used alongside balloon therapy. The choice of combined interventions depends on the cause of bleeding, the patient’s condition, and the available resources. Balloon therapy can provide a window of stability while additional treatments are planned.
Successful use of obstetric balloons depends on clinical training and experience. Healthcare providers must be familiar with device placement, inflation techniques, and monitoring requirements. Training helps ensure that balloons are used effectively and that complications are identified early. In addition, standardized protocols and simulation training can improve team coordination during PPH emergencies. As a manufacturer, Ningbo Yuxin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. supports clinical needs by providing respiratory and gynecological consumables that are produced under controlled conditions, and OEM customization can help meet specific clinical requirements for balloon design and packaging.
OEM customization can support the development of obstetric balloons that match specific clinical requirements, including different sizes, shapes, and inflation capacities. Customization can also extend to packaging, labeling, and accessory design to meet local regulations and clinical preferences. Companies with advanced production capabilities and testing environments can offer tailored solutions for hospitals and healthcare providers. Ningbo Yuxin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. has production equipment such as silicone injection molding machines and plastic injection molding machines, which support the manufacturing of silicone and plastic accessories. Customization allows the company to respond to clinical demands and support a range of obstetric and respiratory applications.
When procuring obstetric balloons, hospitals consider factors such as product specifications, quality control, and supply stability. Consistency in manufacturing and reliable testing are important to ensure the devices perform as expected. A controlled production environment, such as a clean workshop, helps reduce the risk of contamination and supports product reliability. Hospitals also consider training requirements and compatibility with existing clinical protocols. The availability of OEM customization can help hospitals obtain devices that align with their specific workflow and clinical needs. Overall, obstetric balloons are an important component in PPH management when used appropriately and integrated into a comprehensive treatment strategy.
FAQ
Q: What clinical situations make obstetric balloons a preferred option in postpartum hemorrhage management?
A: Obstetric balloons are often used when uterine atony or placenta-related issues lead to continued bleeding after delivery. They are considered when initial measures such as uterine massage and uterotonic drugs do not fully control the bleeding, and when a rapid mechanical compression method is needed to stabilize the patient. In cases where the placenta is abnormally attached or retained, balloons can provide temporary control while additional interventions are planned.
Q: How does the material selection for obstetric balloons affect their performance and safety?
A: Material selection influences factors such as elasticity, pressure tolerance, and biocompatibility. Medical-grade silicone and plastic materials are commonly used to ensure flexibility and safe contact with body tissues. Consistent manufacturing processes and strict testing help ensure that balloons maintain integrity during inflation and do not leak. A controlled production environment, such as a clean workshop and professional laboratory testing, supports the quality of these devices.
Q: What are the main differences between cervical dilation balloons and uterine balloons in clinical use?
A: Cervical dilation balloons are designed primarily to assist in cervical opening and can also support bleeding control in certain scenarios. Uterine balloons are designed specifically to apply pressure within the uterine cavity to reduce bleeding. The choice between them depends on the clinical need, such as whether cervical dilation is required or whether direct uterine compression is the primary goal.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when determining the inflation volume and pressure for an obstetric balloon?
A: Inflation volume and pressure depend on the size of the uterine cavity, the severity of bleeding, and the patient’s response. The goal is to achieve sufficient compression to reduce bleeding while avoiding excessive pressure that could cause discomfort or tissue damage. Clinicians monitor bleeding, uterine tone, and vital signs to adjust inflation parameters. Proper monitoring and gradual adjustment help maintain a balance between effectiveness and safety.
Q: How does OEM customization support the use of obstetric balloons in different healthcare settings?
A: OEM customization allows manufacturers to tailor balloon size, shape, inflation capacity, and packaging to meet specific clinical requirements and local regulations. Customization can also support the integration of accessories or connection ports that align with hospital protocols. Companies with advanced production equipment and clean workshop environments can provide tailored solutions to meet the needs of different healthcare settings.
Q: What are the main monitoring requirements after an obstetric balloon is placed?
A: After placement, monitoring includes regular assessment of vital signs, bleeding volume, uterine tone, and signs of balloon displacement or leakage. The clinical team also observes for potential complications such as infection or pressure-related issues. The duration of balloon placement is determined based on the patient’s condition and response to treatment, and the device may be adjusted or removed if bleeding persists or if adverse signs appear.
Q: How are obstetric balloons integrated into a comprehensive postpartum hemorrhage treatment plan?
A: Obstetric balloons are typically used as part of a broader treatment strategy that may include uterotonic drugs, fluid resuscitation, blood transfusion, and surgical or interventional procedures if needed. Balloons can provide temporary stabilization and reduce bleeding while other interventions are arranged. The integration of balloon therapy depends on the cause of bleeding, patient stability, and available resources, with the goal of controlling hemorrhage and supporting recovery.
Q: What are the considerations for storage and handling of obstetric balloons to ensure readiness in emergencies?
A: Obstetric balloons should be stored in a clean, dry environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Packaging should remain intact to prevent contamination. Regular inventory checks help ensure that devices are available when needed. Proper handling and training help ensure that the device can be deployed quickly and correctly during postpartum hemorrhage emergencies.